In recent years, experts from around the world have noted an increase in degenerative-dystrophic processes in the ankle, which gradually lead to disability. Osteoarthritis of the ankle joint often develops as a result of serious injuries or permanent microtraumas in athletes, professional dancers, circus artists. How to notice the signs of this disease in time and stop its progression, as well as how to treat it, you will learn from this article.
Osteoarthritis of the ankle - what is it
The ankle is a complex block joint formed by the lower (distal) ends of the tibia and fibula of the lower leg, forming the inner and outer ankles (ankle) as well as the talus of the foot. It is strengthened internally by the deltoid ligament, externally by the anterior and posterior talofibular and calcaneofibular ligaments. Function: flexion and extension of the foot. The ankle is functionally connected to the foot, has common connections and muscle tendons with the joints of the foot.
Osteoarthritis of the ankle joint is a degenerative-dystrophic disease that begins with thinning and destruction of articular cartilage, reduction of its cushioning properties, followed by the inclusion of all other joint tissues in the pathological process. The disease gradually leads to complete wear and tear of the joint and disability. The ICD-10 code for ankle osteoarthritis is M19.
The disease is less common than such a knee lesion and is usually the result of serious injury or prolonged injury as a result of any activity.
Causes of osteoarthritis of the ankle
Specialists have studied in detail the reasons for the development of ankle osteoarthritis and osteoarthritis of the foot. This:
- injuries - intra-articular fractures of the joints, fractures of the ankles, complete and incomplete ruptures of ligaments and tendons;
- microtraumas due to any professional activity - these are ballerinas, dancers, professional athletes;
- increased load on the legs with excess weight;
- improper load distribution when wearing high heels;
- metabolic disorders that have a negative effect on the metabolism in cartilage tissue - diabetes, obesity, gout and others. ;
- hormonal, including age-related, changes;
- transferred severe acute purulent arthritis;
- prolonged chronic arthritis of any origin;
- osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine and intervertebral hernia, causing damage to the spinal roots and weakening of the muscles of the lower leg and foot, leading to instability and joint injuries.
Mechanism of disease development (pathogenesis)
Under the influence of various causes, the blood circulation in the joint area is disturbed, which leads to a decrease in the volume of synovial fluid that feeds the cartilage tissue. Due to the lack of oxygen and nutrients, the cartilage becomes thinner, cracks and erosions appear on it. This leads to injury to the cartilage layer of the bone. It thickens (scleroses) and grows on the edges of joint surfaces. These growths are called osteophytes. They compress the soft tissues, blood vessels and nerves, causing pain and further disrupting blood circulation.
Due to circulatory disorders and high tension, muscles suffer, they are weakened, leading to joint instability and frequent sprains. Osteoarthritis of the foot develops, small joints of the tarsus, metatarsal-tarsal, metatarsophalangeal and interphalangeal joints are affected.
Gradually, connective tissue grows in the joints, which connects the joint surfaces tightly and impairs joint function. The complete loss of ankle function is associated with the fusion of the bony joints. Osteoarthritis of the foot gradually develops.
Symptoms of ankle osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis of the ankle is slow and imperceptible at first. But the symptoms gradually appear and increase, signaling some kind of disorder in the lower limb.
First signs
The first symptom of ankle osteoarthritis is pain during heavy loads, such as prolonged walking, dancing, playing football or volleyball, etc. This pain passes quickly, so the person does not pay attention to it immediately, attributing it to muscle fatigue. The pain can be both symmetrical in both joints (under heavy loads and microtraumas) and unilateral (after severe injury).
Then there is a feeling of stiffness in the morning or after a long stay still. The ankles become hard for a while, which makes it difficult to move. In the initial stages it lasts a few minutes and passes after a slow pace. This symptom should already warn and become a reason to visit a doctor.
Obvious symptoms
Gradually the pain after exercise intensifies and lasts longer. The leg can hurt all day. Nocturnal pains join, usually occurring in the second half of the night and are sometimes accompanied by painful muscle cramps. Periods of stiffness after immobilization are also prolonged.
Due to severe pain, a person begins to limp while walking, trying to reduce the pain in the foot by stretching or pressing it. Sometimes the ankle swells, the skin above it becomes red, the pain intensifies. This is a sign of synovitis - inflammation of the inner synovial membrane. Inflammation is non-infectious in nature, develops from mechanical irritation and resolves on its own without treatment. But at the same time the exacerbation of synovitis activates the progression of the joint degenerative-dystrophic process.
Dangerous symptoms
Persistent excruciating pain, aggravated by exercise, instability, joint loosening, tendency to subluxations, dislocations, and ligament injuries are dangerous symptoms that require a visit to the doctor. The ankle changes externally: it acquires a different shape due to overgrown osteophytes. Osteoarthritis of the ankle (ankle) leads to its thickening. The movements in the foot are initially slightly limited, and then the ankle becomes immobile or, conversely, relaxed, unstable. But even at this stage you can help the patient, you just need to contact the clinic. Symptoms of osteoarthritis of the foot appear: pain in the foot, impaired flexion and cushioning. The development of osteoarthritis of the big toe is accompanied by pain and deformity of the foot in the form of protrusion and bending of the big toe outward.
What is dangerous osteoarthritis of the ankle
The danger is that the disease initially develops imperceptibly and very often the patient goes to the doctor at an advanced stage.
Each location and form of osteoarthritis has serious complications, so you should not delay treatment.
Classification
Osteoarthritis of the ankle can be primary, when the cause of its development is not established, and secondary, with a known cause of origin. Depending on the cause of the development, the disease may have its own characteristics.
Post-traumatic arthrosis of the ankle joint
The consequences of a traumatic injury are the most common cause of the disease. Post-traumatic osteoarthritis of the ankle joint can develop after a severe injury - rupture of a ligament, dislocation, intra-articular fracture. Usually one joint is injured, so post-traumatic osteoarthritis is unilateral. A small but untreated injury may not be felt at first. And only after some time, when a person has already forgotten about it, a slight growing pain appears. This type of injury is dangerous because the patient goes to the doctor already in a neglected state. Serious injuries are better treated, their consequences appear faster and the patient seeks medical help not so late.
The inconspicuous prolonged microtrauma of both ankles is typical for professional dancers, athletes and people whose profession is associated with long stays on their feet. There is symmetrical pain in the ankles during exercise. They are usually confused with muscle aches and fatigue, so it is also too late to see a doctor.
Osteoarthritis of the ankle after arthritis
The causes of these arthrosis can be chronic inflammatory processes in the joints (arthritis): rheumatoid, reactive, psoriatic. In this case, the inflammatory processes are combined with degenerative-dystrophic (arthritis-arthritis). This speeds up the process of breaking the ankle. With exacerbation of inflammation, the joints swell, the skin above them becomes red, the pain becomes very strong, especially at night. When the inflammation subsides, metabolic disorders predominate, while all processes develop very quickly. The disease requires constant monitoring and treatment by a rheumatologist.
Much less often, the degenerative-dystrophic process develops after acute purulent arthritis. The purulent process destroys the joint tissues and after restoration in their place connective tissue is formed, which disrupts the function of the limb.
Osteoarthritis can also form after infectious arthritis - tuberculosis, gonorrhea and others. The progression of the disease is related to the underlying infectious process and the nature of the destruction. If the infection persists, the destruction of the joints will progress.
Metabolic
It develops with prolonged gout. The first toe is very often affected. Other small joints of the foot and ankle are less commonly affected. As gout attacks continue, it is difficult to determine externally when the degenerative-dystrophic process occurs. You can only see it on an X-ray. In any case, the patient should be monitored regularly by a rheumatologist and periodically examined.
Deforming arthrosis of the ankle joint
All types of osteoarthritis deform over time. Bone deformities indicate an advanced stage of the disease, when the cartilage has already collapsed and the constant mechanical impact on the bone tissue contributes to its growth along the edges of the joint surface. This forms osteophytes that change the shape of the joint.
Degrees of arthrosis of the ankle joint
There are several classifications, one of which distinguishes three clinical and radiological stages of osteoarthritis:
- early. Slight soreness after standing or walking for a long time, some stiffness in the morning. All this disappears quickly without any help. X-ray: normal or slight narrowing of the joint space.
- progressive. The pain after exercise is stronger and longer. Stiffness increases, crunch occurs during movement. Sometimes the joint swells, reddens and hurts a lot - a sign of synovitis. The X-ray shows a significant narrowing of the joint space, thickening of the cartilaginous bone tissue (osteosclerosis) and proliferation of osteophytes.
- Final. The pain syndrome intensifies, becomes permanent. Because of the pain, a person is lame, puts his feet away, uses a cane or crutches. Limb function is impaired, osteoarthritis of the foot and toe develops. The complete absence of flexion-extensor movements is rare, usually against the background of osteoarthritis. On X-ray: no joint space, osteosclerosis, large osteophytes deforming the joint.
Possible complications
If the disease is not treated and everything is fine, then the following complications are possible:
- persistent joint dysfunction and damage;
- severe constant pain in the ankle and feet, both after and without exertion;
- ankle instability with the development of common dislocations and subluxations;
- damage to the foot and toe will join, which will further worsen the patient's condition.
Diagnosis of ankle osteoarthritis
Before prescribing treatment, the doctor examines the patient, including:
- medical interview and examination;
- additional methods of examination: laboratory tests (signs of inflammation and metabolic disorders are detected), instrumental tests (radiography of the joint in two projections, computer and magnetic resonance imaging - early changes in bone structures and soft tissues are detected), diagnostic arthroscopyexamines the inner joint surface).
Treatment of ankle osteoarthritis
After establishing the final diagnosis, the doctor chooses an individual treatment complex for the patient, consisting of medicinal and non-medicinal methods.
Drug treatment of osteoarthritis of the ankle joint
Drugs are prescribed that have a symptomatic (eliminates the symptoms of the disease) and pathogenetic (suppresses the mechanism of disease development) effect.
Anti-inflammatory and analgesic
To eliminate the pain, short-term drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are prescribed, which relieve pain and inflammation well (if the synovitis has worsened):
- injection;
- rectal suppositories;
- tablets for oral administration;
- each patch.
Muscle relaxants
The muscles surrounding the diseased joint and carrying out its movement are in constant tension, which leads to their atrophy and intensification of pain. Drugs from the group of muscle relaxants are prescribed to eliminate muscle spasms.
Chondroprotectors
Chondroprotective drugs contain glucosamine or chondroitin, and sometimes both. They protect cartilage cells from destruction and promote their recovery. They are prescribed in the form of injections, tablets and external means (creams and ointments).
Preparations with hyaluronic acid for osteoarthritis of the ankle joint
To improve the amortization capacity of synovial fluid and prevent further injury to cartilage and bone tissue, hyaluronic acid is injected into the joint cavity. This relieves pain and improves joint mobility.
Antiarthritis gels and ointments for ankle osteoarthritis
External funds can be used at home. Ointments for osteoarthritis of the ankle joint:
- NSAID gels are suitable for relieving pain and inflammation;
- for cartilage repair - gel and ointment based on chondroitin.
Non-drug therapy
The main methods of treating osteoarthritis of the ankle are non-drug. These are healing exercises, massage, physiotherapy, wearing orthopedic devices.
Physiotherapy
To alleviate the patient's condition and restore joint function are prescribed:
- drug electrophoresis;
- laser therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- warming procedures - paraffin, ozokerite, in the conditions of resorts - mud applications.
Massage for osteoarthritis of the ankle joint
Massage courses improve blood circulation, which leads to activation of metabolism, recovery of joint and extra-articular tissues. The positive effect of massage on the muscles is the elimination of spasms, which contributes to the flow of blood to the muscles and the restoration of their strength needed to keep the limb in the desired position.
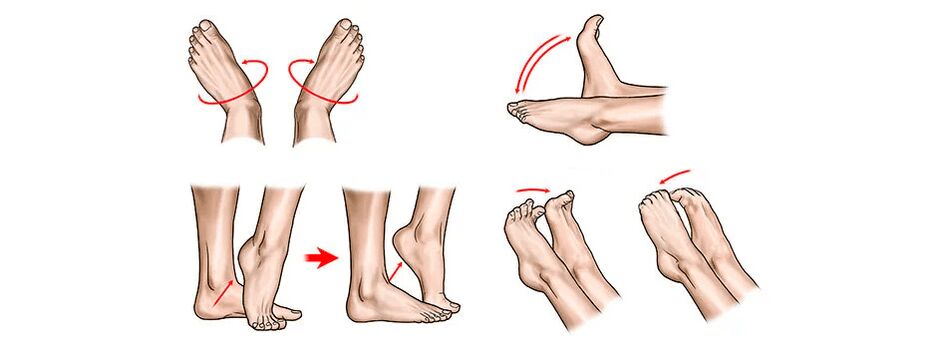
Exercises and exercise therapy for osteoarthritis of the ankle joint
Therapeutic gymnastics is a panacea for osteoarthritis. Physical activity is very important, in addition to therapeutic exercise, swimming is useful. Systematic performance of exercises selected by the doctor allows you to largely restore limb function, even in advanced disease.
Approximate set of exercises (but before starting it, you should consult your doctor):
Use of special orthopedic products
To prevent the progression of the disease, the doctor may prescribe wearing a special orthopedic device - an orthosis. Fixes the legs in the correct anatomical position, relieves muscle tension, improves blood circulation. Wearing an orthosis is prescribed by a doctor who chooses the most appropriate model.
The fixation of the ankle can also be done with the help of adhesive tape: with special adhesive tapes, the ankle is carefully fixed in the desired position.

Surgical intervention
Surgery is recommended for severe pain that is not eliminated by conservative treatment, as well as for significant limb dysfunction.
Types of surgical interventions
Operations can be performed in traditional and gentle ways:
- Therapeutic arthroscopy (gentle surgery):
- Rehabilitation of the joint cavity - with the help of an arthroscope from the cavity are removed fragments of cartilage and bone tissue that impede movement and cause pain;
- chondroplasty - the damaged layer of cartilage is removed, which stimulates the growth of new cartilage cells (abrasive chondroplasty); in some cases, transplantation of areas of cartilage taken from unloaded areas of the patient's knee joint (mosaic arthroplasty) is performed; Chondroplasty is effective in stage 2 disease, when the joint has not yet lost its function.
- Arthrodesis is a traditional surgical operation. It is performed with significant impairment of limb function, slackness, normal sprains and pain. The joint is removed, the bones of the lower leg merge with the bones of the foot. The ankle becomes immobile and serves only as a support.
- Endoprosthesis is the replacement of worn and lost ankle function with an artificial one.
Characteristics of rehabilitation after surgery
All operations are performed in an inpatient setting, after which experts recommend complete rehabilitation. In sparing operations, rehabilitation is performed on an outpatient basis with early inclusion in the course of therapeutic exercises with the exception of high loads on the joint. After endoprosthesis, the patient remains in the hospital for one week, and then rehabilitation measures are carried out on an outpatient basis. After two weeks, the sutures are removed and the patient can take a shower.
Dietary food
There is no special diet for osteoarthritis. But to eliminate unnecessary stress on the ankle, it is necessary to maintain a normal body weight. One should get a proper healthy diet, but the volume of high-calorie foods should be partially replaced by vegetables and fruits. Useful are the first and second dishes of low fat, chicken, sea fish, cottage cheese, cheese, dairy products.
Traditional Medicine
Using only traditional medicine for osteoarthritis will not help. But they can be used as part of a complex treatment prescribed by a doctor. Here are some recipes:
- for oral administration: infusion of wild rosemary; Pour 20 g of finely chopped grass overnight in a thermos with 500 ml of boiling water, strain in the morning and take half a cup 4 times a day for a month; cartilage repair analgesic;
- for oral administration: take a ball of mummy with a diameter of 0, 5 cm in the morning, chewing thoroughly, 30 minutes before meals for 10 days; rest 5 days, then repeat everything 3 more times; excellent stimulator of metabolic processes;
- honey massage: apply warm liquid honey on the ankle before bed and rub lightly, massaging the tissues for 5 minutes; then wrap your legs in a warm scarf and leave until morning; restores blood circulation and metabolism in cartilage tissue.
Approach to treatment in clinics
Doctors at the clinic have developed their own approach to treating diseases such as osteoarthritis of the ankle and foot. During the initial appointment, the patient is thoroughly examined, the doctor carefully listens to his complaints and medical history, and then prescribes additional laboratory and instrumental tests, including MRI. Only then the doctor establishes the final diagnosis, prescribes and agrees with the patient a comprehensive treatment. Consists of:
- modern schemes for medical and non-medical treatment of osteoarthritis - drugs, physiotherapy, exercise therapy and massage, methods for fixing the ankle;
- traditional methods of oriental therapy - acupuncture, moxibustion, acupressure, various methods of kinesiotherapy, including taping.
These are not all the methods used in clinics. Doctors are able to combine Western and Eastern methods, significantly accelerating the improvement of the patient's condition. Patients quickly get rid of pain, their quality of life improves significantly.
Combined proven techniques of the East and innovative methods of Western medicine.
Prevention of osteoarthritis of the foot
To reduce the risk of disease progression, the following recommendations should be followed:
- activity, physical therapy exercises, swimming should become part of your life;
- high physical activity and any traumatic factors should be excluded; hiking should be combined with rest, if the legs are injured during work, then it is worth changing it;
- injuries, especially in the winter on ice, must be ruled out, considering the manner of movement and the shoes used;
- rational nutrition is necessary to restore metabolism, but being overweight is an additional burden on the ankle, get rid of it;
- preventive treatment courses are a guarantee of a pain-free life.
Frequently asked questions about the disease
- Which doctor should I go to for osteoarthritis of the ankle and foot osteoarthritis?
At the orthopedist-traumatologist. But if the disease develops against the background of some rheumatic process, then a rheumatologist.
- What predictions do doctors usually give?
It is possible to stop the progression of the degenerative process and improve the quality of life at any stage, but it is best to do this at the beginning of the disease, do not wait for complications.
- Can ankle osteoarthritis develop in children?
Maybe after an injury or on the background of congenital pathology.
- What are the consequences of the disease?
Untreated osteoarthritis leads to disability. If you start treatment on time, it is quite possible to maintain limb function. Treatment in the later stages will relieve pain and improve quality of life.
- Are sports injuries the cause of osteoarthritis of the ankle?
Yes, sports injuries are one of the main causes of this disease.
- Is it possible to tape the ankle in osteoarthritis?
It is possible, but this must be done by a specialist.
Osteoarthritis of the ankle joint is almost always the result of macro- or microtrauma. At first it is slow and imperceptible. That is why timely treatment and rehabilitation after injuries is as important as contacting a doctor at the first signs of ankle disease.































